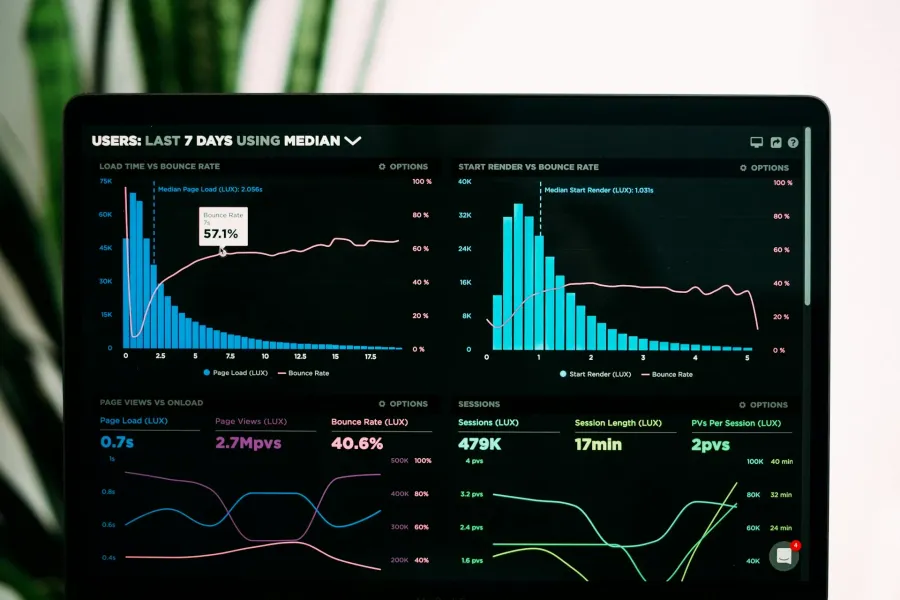
What is Content Cannibalization?
TL;DR
Content cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your website target the same keyword or topic, forcing them to compete against each other in search results. Instead of one strong page ranking well, you end up with two or more weaker pages that split backlinks, authority signals, and click-through rate. The result: none of your pages rank as well as a single consolidated page would.
On this page
Why Content Cannibalization Matters
Cannibalization is one of the most common (and most overlooked) SEO problems. It's especially prevalent on:
- Blogs that have covered similar topics multiple times over years
- E-commerce sites with similar product variations or overlapping category pages
- Service businesses with pages for different locations using the same service content
- Sites after redesigns where old pages weren't properly redirected
Why it hurts rankings:
Split authority: If you have 10 backlinks to Page A and 5 to Page B on the same topic, neither page has the combined authority of 15 backlinks.
Confused crawl signals: Google can't determine which page is your "canonical" resource, so it picks one, often not the one you'd prefer.
Diluted CTR: When both pages appear in search results (or alternate between results), clicks are split between them.
Wasted crawl budget: Googlebot crawls multiple similar pages instead of discovering unique content.
Real impact: I've seen sites jump from page 2 to position 3 simply by consolidating 3 cannibalizing pages into one.
How Content Cannibalization Works
How to diagnose cannibalization:
Method 1: Google Search Console
- Go to Performance → Pages
- Click a page, then click "Queries"
- For each query, check if multiple pages from your site rank
- If different pages rank for the same query at different times, they're cannibalizing
Method 2: Site Search
Search site:yourdomain.com "target keyword" in Google. If multiple pages appear that seem to target the same intent, investigate further.
Method 3: SEO Tools
Ahrefs and Semrush can show which of your URLs rank for the same keyword. Look for URLs with overlapping keyword profiles.
Cannibalization vs. Intentional Topic Clusters:
Not all overlap is cannibalization. A pillar page on "plumbing services" and a cluster page on "drain cleaning services" serve different intents and support each other. True cannibalization is when pages target the same intent and compete directly, like having both "10 Plumbing Tips" and "Top Plumbing Tips for Homeowners."
Cannibalization Solutions
| Type | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Merge + 301 | Combine competing pages into one comprehensive page | When pages cover same topic from same angle |
| Differentiate | Refocus each page on a distinct search intent | When pages could serve different user needs |
| Canonical Tag | Point cannibalizing pages to the preferred version | When duplicate pages must exist (e.g., faceted navigation) |
| Noindex | Keep page accessible but remove from search index | When a page serves users but shouldn't rank |
Content Cannibalization Best Practices
-
Audit for cannibalization before creating new content. Check if you already have a page on the topic that could be updated instead of creating a new one.
-
Use a keyword mapping document. Track which keyword(s) each page targets. If two pages have the same target keyword, you've identified cannibalization.
-
When merging, choose the page with more backlinks as the survivor. 301 redirect the others to preserve link equity.
-
After merging, update internal links across your site to point to the consolidated page. Don't leave internal links pointing to redirected URLs.
-
Consider user intent carefully. Two pages on 'plumbing costs' might not be cannibalizing if one targets 'plumber hourly rates' (informational) and one targets 'plumber service call cost' (commercial).
-
Monitor after fixing. Check Search Console to confirm the consolidated page now ranks for all the keywords the separate pages used to target.
Common Content Cannibalization Mistakes to Avoid
-
Assuming all topic overlap is cannibalization. Topic clusters intentionally overlap. That's how Topical Authority works. The issue is when pages target identical intent, not just related topics.
-
Deleting pages without redirecting. If a cannibalizing page has backlinks, deleting it loses that link equity. Always 301 redirect to the surviving page.
-
Using canonical tags as a lazy fix. Canonical tags are a hint, not a directive. Google may ignore them if pages are too different. For true duplicates, 301 redirects are more reliable.
-
Merging without improving. The consolidated page should be better than either original, not just longer. Add new information, update outdated sections, improve the structure.
-
Forgetting about internal links. After consolidating pages, every internal link to the old URLs should be updated to point to the new URL directly (not through redirects).
Recommended Content Cannibalization Tools
Connect Screaming Frog to Search Console to see which URLs rank for which queries. Export and filter for overlapping keywords.
View organic keywords for any page. Compare keyword profiles between pages to identify overlap.
Dedicated cannibalization detection within SEMrush's Position Tracking tool.
Create a keyword mapping spreadsheet: URL, target keyword, secondary keywords. Manual but forces intentional planning.
Frequently Asked Questions About Content Cannibalization
How do I know if fluctuating rankings are due to cannibalization?
Check which URL ranks for the query over time. In Search Console, filter by a specific query and view by Page. If you see different URLs appearing on different days, those URLs are cannibalizing each other. Google is testing which is most relevant.
Can cannibalization affect pages on different subdomains?
Yes. blog.example.com and www.example.com can cannibalize each other. Google treats subdomains as somewhat separate but still recognizes they're the same organization competing against itself.
Should I worry about pages ranking for the same keyword in positions 1 and 5?
If both are your pages, yes. Investigate. Sometimes Google shows two results from the same site for a query, but one is usually a featured result type (like a video or FAQ). If they're both standard results targeting the same intent, consolidating would likely put the combined page at position 1 more consistently.
What if cannibalizing pages have significantly different content?
If the content is genuinely different, the pages might be targeting different intents that you haven't clearly differentiated. Refine each page's focus so it clearly serves a distinct search intent. Add intent-specific keywords and restructure content to match.
How long after fixing cannibalization will I see ranking improvements?
Typically 2-8 weeks. Google needs to recrawl the consolidated page, process the redirects, and reassess rankings. The more competitive the keyword, the longer it may take. Track progress in Search Console.
Terms Related to Content Cannibalization
301 Redirect
A permanent redirect that tells browsers and search engines "this page has moved forever, go here instead." When someone...
Read definition SEOCanonical Tag
An HTML element that tells search engines which version of a page is the "main" one. If you have similar content accessi...
Read definition SEOKeyword Research
Finding out what your potential customers are already searching for, then building content that shows up when they searc...
Read definition SEOSearch Intent
The purpose or goal behind a user's search query. Understanding search intent is critical for Keyword Research and On Pa...
Read definition SEO302 Redirect
A temporary redirect that tells search engines "this page has moved for now, but it's coming back." Unlike a 301 Redirec...
Read definition SEOAlgorithm
The complex set of rules Google uses to rank websites. Google updates its algorithm thousands of times per year, with ma...
Read definitionFeatured SEO Case Study

How a CPA Firm Captured 991 Top-3 Google Rankings and 175 AI Overview Citations
Strategic website redesign and content architecture helped an established Colorado Springs CPA firm dominate both traditional search and AI-powered results, with 991 keywords in the top 3 and 175 AI Overview citations.
More SEO Case Studies
 Featured
Featured
Local SEO Case Study: From Invisible to #1 Across 100 Miles in 6 Days
From invisible to #1 across 100 miles in 6 days

How 50 Monthly Searches Turned Into a Fully Booked Consulting Business
From zero online presence to fully booked in 6 months, zero ad spend
Secrets of the Tribe: From Basic Template to 49 Position 1 Rankings in 3 Months
#1 on Google for 49 searches in just 3 months

E-commerce SEO Case Study: From $28,800 in Annual Ad Spend to 7,500+ Monthly Organic Visitors
Stopped paying $2,400/month in ads, now gets 7,500 visitors free
 Featured
Featured
How a Forced Name Change Became the Best Thing That Happened to a Colorado Springs Epoxy Company
From invisible online to #1 across a 25-mile radius, fully booked, and expanding into commercial
Website Redesign for a Regenerative Medicine Clinic That Actually Converts
Patients now book online instead of calling to ask questions
Ready for Results Like These?
Let's talk about how seo can drive real growth for your business.
Get a Free ConsultationSEO Articles
View All Posts »The Complete SEO Guide for Small Businesses (2026)
Everything a small business owner needs to know about SEO in 2026. Real strategies, honest timelines, and actual results from businesses like yours.
How to Build a Local SEO Strategy That Actually Works in 2026
A comprehensive guide to local SEO in 2026, covering Google Business Profile optimization, citation building, review management, and the tactics that actually move rankings for small businesses.
SEO vs PPC – How to Choose the Right Strategy for Your Small Business Marketing
Should you invest in SEO or PPC for your small business? This comprehensive guide breaks down both strategies, their costs, benefits, and when to use each.
SEO Guide: Google's 2025 Quality Guidelines Explained for Business Owners
Learn how Google's E-E-A-T quality guidelines actually work and how to use them to outrank competitors in local search results.
10 Website Design Mistakes Killing Your SEO (2025)
Discover the most common website design mistakes that hurt your SEO rankings and learn how to fix them for better traffic and conversions.